Residential Solar Panel Installation in Japan – Process and Key Considerations
Residential solar panel installation in Japan follows structured procedures to ensure safe and compliant setup in homes. The process typically includes site assessment, system design, installation by certified technicians, and connection to the local grid. Attention is placed on safety, regulatory compliance, and alignment with national energy standards to provide a clear framework for households adopting solar technology.
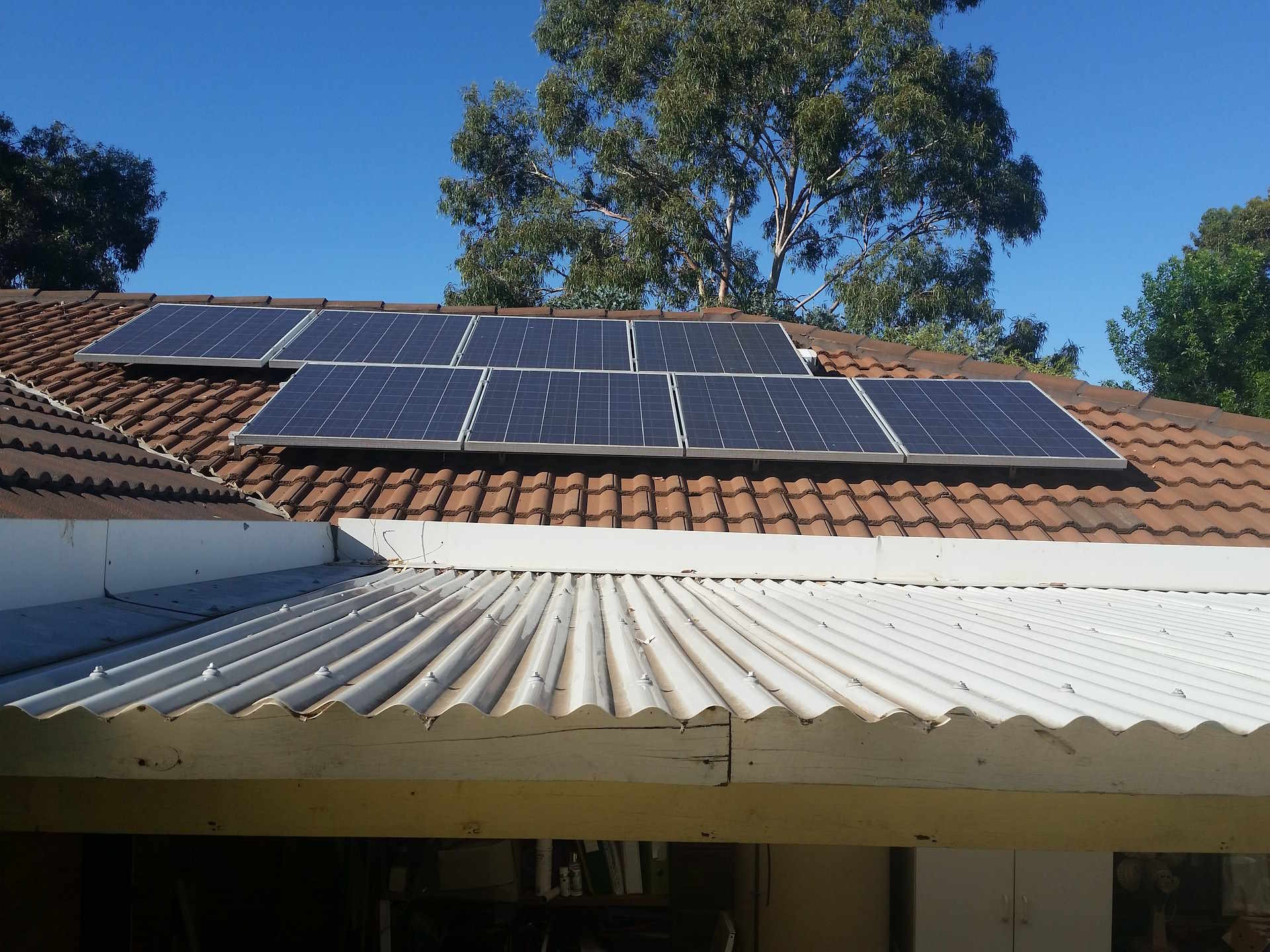

What are the steps in residential solar panel installation in Japan?
The process of installing solar panels on a residential property in Japan typically involves several key steps:
-
Initial consultation and site assessment
-
System design and quotation
-
Permitting and paperwork
-
Equipment procurement
-
Installation
-
Inspection and grid connection
-
System activation and monitoring
Each step requires careful planning and coordination between homeowners, solar installers, and local authorities to ensure a smooth and compliant installation process.
How is site assessment and system design conducted?
Site assessment and system design are crucial components of the solar panel installation process in Japan. During the site assessment, certified solar technicians evaluate various factors:
-
Roof condition, size, and orientation
-
Shading analysis
-
Structural integrity of the building
-
Electrical system capacity
Based on this assessment, designers create a customized solar system plan that maximizes energy production while adhering to local building codes and regulations. The design typically includes the number and placement of panels, inverter specifications, and wiring diagrams.
What role do certified technicians play in the installation process?
Certified technicians are essential to ensure proper installation and compliance with Japanese safety standards. These professionals undergo rigorous training and certification processes to stay updated on the latest solar technologies and installation practices.
During the installation, certified technicians are responsible for:
-
Safely mounting solar panels on the roof
-
Installing and configuring inverters
-
Establishing proper electrical connections
-
Implementing safety measures such as grounding and surge protection
Their expertise helps minimize the risk of installation errors that could impact system performance or pose safety hazards.
How is the solar system connected to the local power grid?
Connecting a residential solar system to the local power grid in Japan involves several steps:
-
Coordination with the local utility company
-
Installation of a bi-directional meter
-
Implementation of grid-tie inverter technology
-
Establishment of a power purchase agreement (if applicable)
The grid connection allows homeowners to feed excess energy back into the grid, potentially earning credits or compensation through net metering programs. It also ensures a stable power supply when solar production is insufficient to meet household demand.
What are the regulatory compliance and energy standards in Japan?
Japan has established comprehensive regulatory frameworks and energy standards for residential solar installations:
-
Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law (DENAN)
-
Building Standard Law
-
Fire Service Act
-
Feed-in Tariff (FIT) program regulations
Compliance with these standards is mandatory and ensures the safety, reliability, and efficiency of solar installations. Additionally, Japan’s energy efficiency standards promote the use of high-quality solar equipment that meets specific performance criteria.
What are the typical costs and available incentives for solar installation in Japan?
The cost of residential solar panel installation in Japan can vary significantly based on system size, equipment quality, and installation complexity. Here’s a general overview of costs and incentives:
| System Size | Estimated Cost Range (JPY) | Potential Annual Savings (JPY) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 kW | 800,000 - 1,200,000 | 40,000 - 60,000 |
| 4 kW | 1,000,000 - 1,500,000 | 50,000 - 80,000 |
| 5 kW | 1,200,000 - 1,800,000 | 60,000 - 100,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Incentives available in Japan include:
-
National-level subsidies for residential solar installations
-
Local government grants and rebates
-
Tax deductions for home improvement loans used for solar installations
-
Feed-in Tariff (FIT) program payments for excess energy production
These incentives can significantly reduce the overall cost of solar panel installation and improve the return on investment for homeowners.
The adoption of residential solar panels in Japan continues to grow as homeowners recognize the long-term benefits of clean energy production. By understanding the installation process, regulatory requirements, and financial considerations, Japanese residents can make informed decisions about transitioning to solar power. As technology advances and installation practices evolve, solar energy is becoming an increasingly accessible and attractive option for sustainable home energy in Japan.