Dental Assistant Training: Role, Skills, and Study Paths
Starting a career as a dental assistant involves structured learning and supervised practice. This overview explains the day‑to‑day responsibilities, what training typically covers, how to review accreditation and practical components, and ways the role can grow across different clinical settings. Use it to understand course content, safety expectations, and the competencies clinics value.
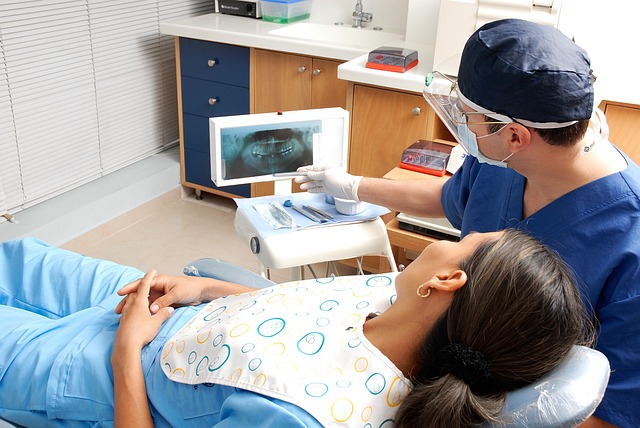
What subjects are covered in dental assistant training?
Dental assistant training programs are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of dental procedures, patient care, and office management. The curriculum typically includes:
-
Dental Anatomy: Students learn about the structure and function of teeth, gums, and oral tissues.
-
Radiography: Training in taking and processing dental X-rays is a crucial component.
-
Dental Materials: Understanding the properties and use of various dental materials is essential.
-
Infection Control: Learning proper sterilization techniques and safety protocols is paramount.
-
Chairside Assisting: This covers assisting dentists during procedures and patient management.
-
Dental Office Administration: Basic office skills, including scheduling and record-keeping, are often included.
These subjects form the core of most dental assistant training programs, ensuring graduates are well-prepared for their roles in dental practices.
How are practical skills developed through labs and clinical practice?
Hands-on experience is a vital aspect of dental assistant training. Most programs incorporate laboratory sessions and clinical practice to reinforce theoretical knowledge and develop practical skills. During lab sessions, students typically:
-
Practice using dental instruments and equipment
-
Learn to take dental impressions and create dental models
-
Simulate chairside assisting techniques
-
Perform mock dental procedures on mannequins
Clinical practice often involves supervised work in actual dental offices or clinics, allowing students to apply their skills in real-world settings. This practical experience is invaluable in building confidence and competence before entering the workforce.
What are the entry criteria for dental assistant training programs?
Entry requirements for dental assistant training programs can vary depending on the institution and location. However, common criteria include:
-
High school diploma or equivalent
-
Minimum age requirement (usually 18 years)
-
Background check and immunization records
-
Basic computer skills
-
Good communication abilities
Some programs may require prerequisite courses in biology, chemistry, or anatomy. It’s important to check with specific institutions for their exact requirements, as they can differ.
How can you review accreditation and assessment methods?
When considering a dental assistant training program, it’s crucial to review its accreditation and assessment methods. Here’s what to look for:
-
Accreditation: Ensure the program is accredited by recognized bodies such as the Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA) in the United States or equivalent organizations in other countries.
-
Curriculum Review: Examine the course outline to ensure it covers all necessary subjects and skills.
-
Assessment Methods: Look for a mix of written exams, practical tests, and clinical evaluations.
-
Instructor Qualifications: Check the credentials and experience of the teaching staff.
-
Graduate Success Rates: Inquire about job placement rates and certification exam pass rates for program graduates.
Reviewing these aspects will help you choose a reputable program that provides quality education and prepares you well for your career.
What career settings and progression opportunities exist for dental assistants?
Dental assistants can work in various settings and have numerous opportunities for career advancement. Common career paths include:
-
Private Dental Practices: The most common setting, offering opportunities to work with general dentists or specialists.
-
Hospitals: Some dental assistants work in hospital dental departments or emergency rooms.
-
Public Health Clinics: These settings often serve underserved populations and can provide valuable experience.
-
Dental Schools: Assisting in educational settings can be rewarding and offer unique learning opportunities.
-
Specialty Practices: Working with orthodontists, oral surgeons, or pediatric dentists can lead to specialized skills.
Career progression often involves:
-
Becoming a senior dental assistant or lead assistant
-
Specializing in areas like orthodontics or oral surgery
-
Pursuing further education to become a dental hygienist or dentist
-
Moving into dental office management or administration
-
Teaching in dental assistant training programs
The dental field offers numerous paths for growth and specialization, making it an attractive career choice for those interested in healthcare and patient care.
Dental assistant training provides a solid foundation for a fulfilling career in oral healthcare. By understanding the training process, required skills, and potential career paths, aspiring dental assistants can make informed decisions about their education and professional development. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance your career, the field of dental assisting offers diverse opportunities for growth and specialization.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




